
As a result of the collective desire for environmental rehabilitation of the Étang de Berre (France’s largest Mediterranean lagoon), the GIPREB (at the time the “Public interest group for the rehabilitation of the Berre lagoon”) was created in 2000.
Since its creation, the role of the GIPREB has been to coordinate the recovery of the Étang de Berre and to define its restoration program. In 2011, the Gipreb evolved into a mixed union structure and is now simply called “Gipreb Syndicat Mixte”. The GIPREBs objectives are to improve the ecological quality of the lagoon complex and in particular to return the Étang de Berre to a state characteristic of a coastal Mediterranean lagoon.
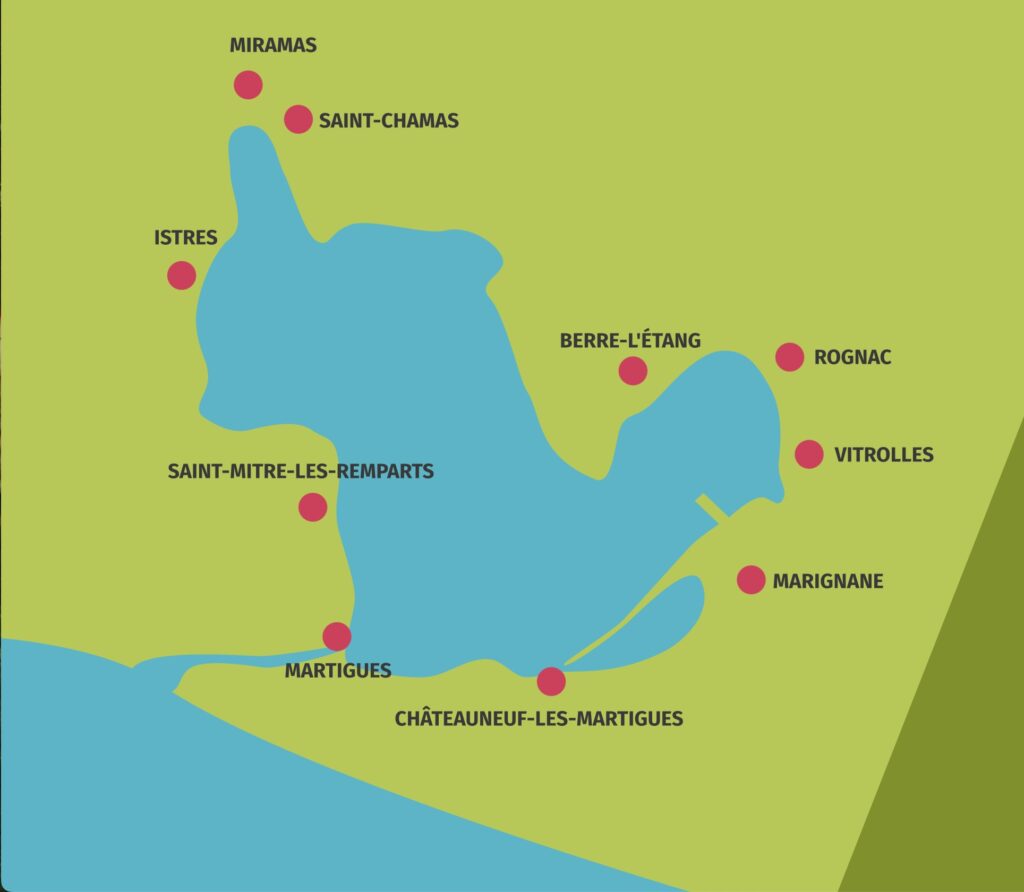
Étang de Berre map ©️ GIPREB
Our shared vision

The Seagrass Consortium works to support the vision for seagrass restoration in the Étang de Berre as defined by the management board of the GIPREB.
Specifically, we seek to support the GIPREB with the restoration of Zostera marina, Zostera noltii and Cymodocea nodosa meadows towards the restoration target of 1,500ha of mixed seagrass meadows.
This is a target set by the la directive-cadre sur l’eau (DCE), which represent a translation of the targets set by the Water Framework Directive (WFD).
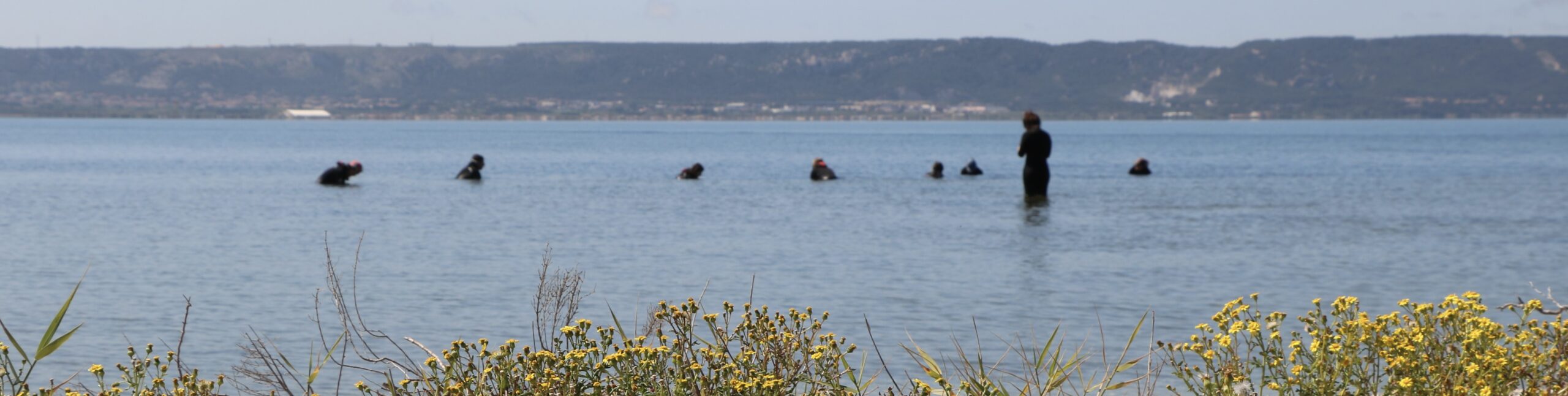

Historical context
| Year | Zostera marina (ha) | Zostera noltii (ha) | Cymodocea nodosa (ha) | Source |
| 1916 | 6000 (estimated) | 2000ha (estimated) | Unknown | Germain (1917) |
| 1965 | 4000 (estimated) | 2000ha (estimated) | Unknown | Mars (1966) |
| 1995 | <1 | 65 | <1 | Pergeant-Martini et al (1995) |
| 2009 | <1 | 1.2 | <1 | GIPREB (2009) |
| 2020 | <1 | 8.2 | <1 | GIPREB (2020) |
| 2021 | <1 | 14.7 | <1 | GIPREB (2021) |
| 2022 | <1 | 25.2 | <1 | GIPREB (2022) |
| 2023 | <1 | 42.6 | <1 | GIPREB (2023) |
| 2024 | <1 | 59.2 | <1 | GIPREB (2024) |
| 2025 | <1 | 70.0 | <1 | GIPREB (2025) |
| Compared to the 1965 ‘baseline’ ; the largest known seagrass meadow surface area. | -99% | –96.5% | 99% |
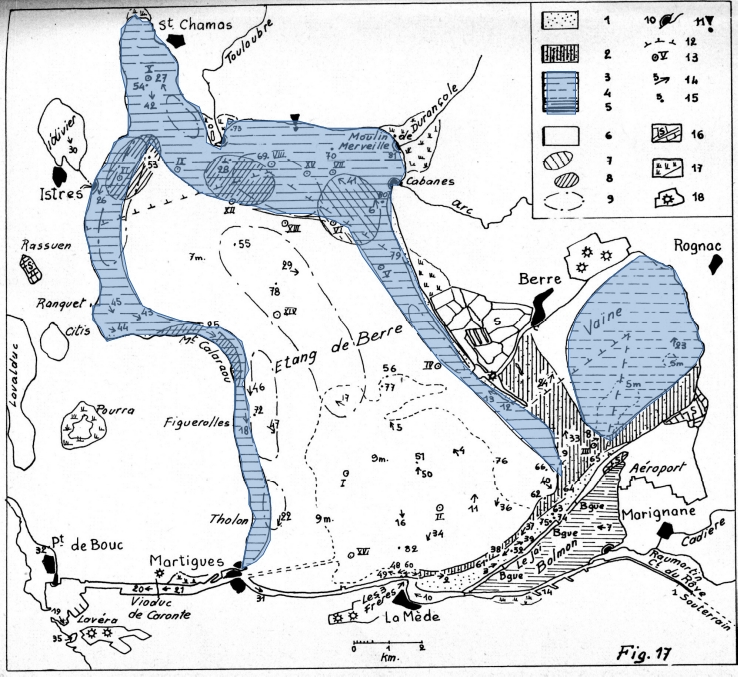
A map of the Étang de Berre from the thesis of Paul Mars (1966). The area shaded in blue corresponds to the area of the ‘seagrass meadows’ reported, although there is no quantitative data relating to the relative ratios of the three species then present in the lagoon.
The thesis records the coastline of the Étang de Berre is as predominantly Zostera marina, whilst the smaller Étang de Vaïne (south east corner of map, surface area of approximately 760ha) had a higher proportion of Zostera noltii.
The historic seagrass areal baselines (estimated in table) are based on 0-3m depth contour which would likely have had a larger proportion of Zostera noltii, and the 3m+ depth contour which would likely have had a greater proportion of Zostera marina). The 1965 data is used as the baseline for our restoration work.
A series of maps showing the evolution of the surface area of the Étang de Berre between 1916 and 2009 has been produced by GIS Posidonie here.
Restoration in numbers – the data.
Key Performance Indicators and milestones we’ve achieved since 2024.
4973
Zostera noltii sods transplanted
Le GIPREB initiated sod-based Zostera noltii restoration within l’Étang de Berre in May 2024 following an agreement being reached for the better management of freshwater discharges into the lagoon.

60
Zostera marina sods transplanted
Le GIPREB initiated a sod-based Zostera marina restoration pilot within l’Étang de Berre following the success of the Zostera noltii restoration pilot in 2024.
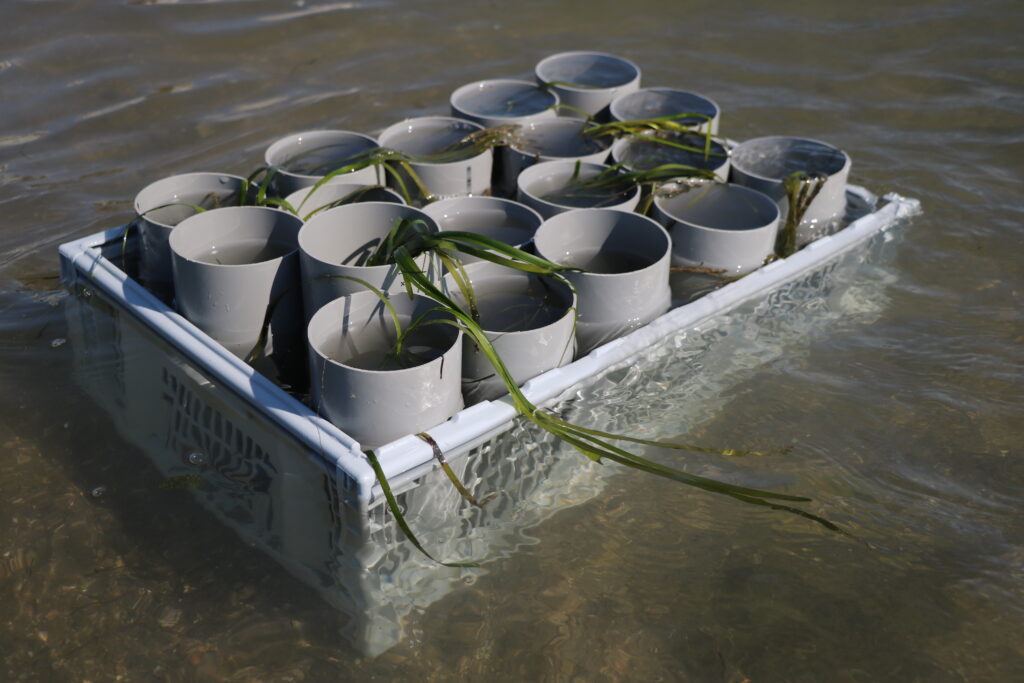

60
Cymodocea nodosa sods transplanted
Le GIPREB initiated sod-based Cymodocea nodosa restoration pliot within l’Étang de Berre following the success of the Zostera noltii restoration pilot in 2024.
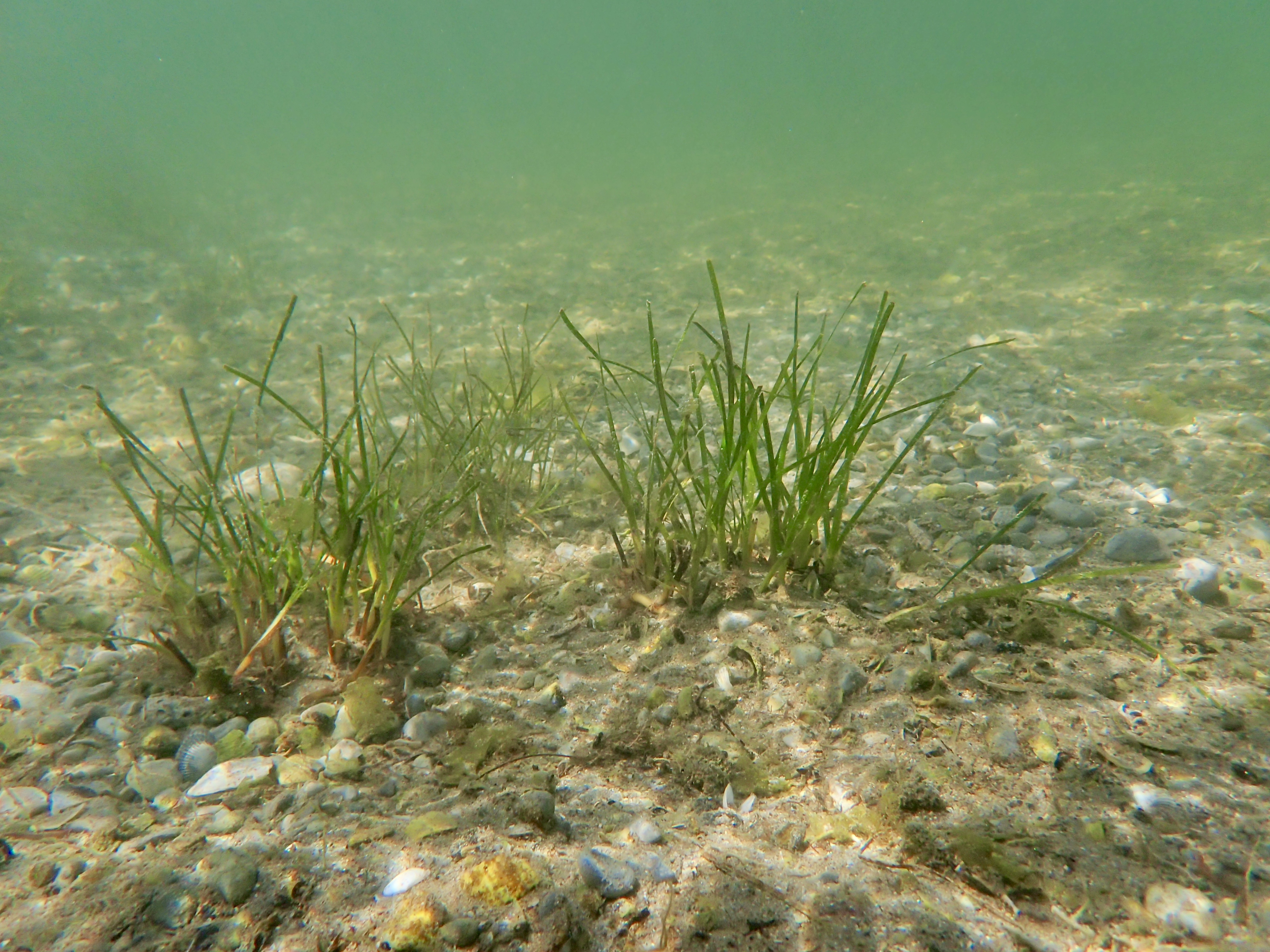


Long-term vision
Key Performance Indicators and milestones we’ve achieved since 2023.

1
Large-scale restoration sites
Within l’Étang de Berre, one ‘large-scale’ (1ha+ restoration sites) has been identified so far. These are locations where sod based restoration is proving successful.
To this end we are now actively transplanting and seeding seagrass at “Batidou”.
- Batidou (800 Zn sods in 2024, 938 Zn sods, 60 Cn sods, 60 Zm sods) in 2025)
4
Test stations
Since 2024 we have transplanted Zostera noltii at 4 additional test sites around the Étang de Berre. This pilot work is enabling us to identify suitable restoration sites for active restoration. Following monitoring in October 2025 we can confirm all 4 sites tested so far are suitable for active restoration.
- Bouquet in 2024 (473 Zn sods)
- La Digue in 2025 (662 Zn sods)
- Boss beach in 2025 (1890 Zn sods)
- Le Canet in 2025 (330 Zn sods)
Discover the Vibrant Restoration Site Gallery
This section features a carefully selected array of images capturing the ‘day-to-day’ actions and the progress of our seagrass restoration efforts.
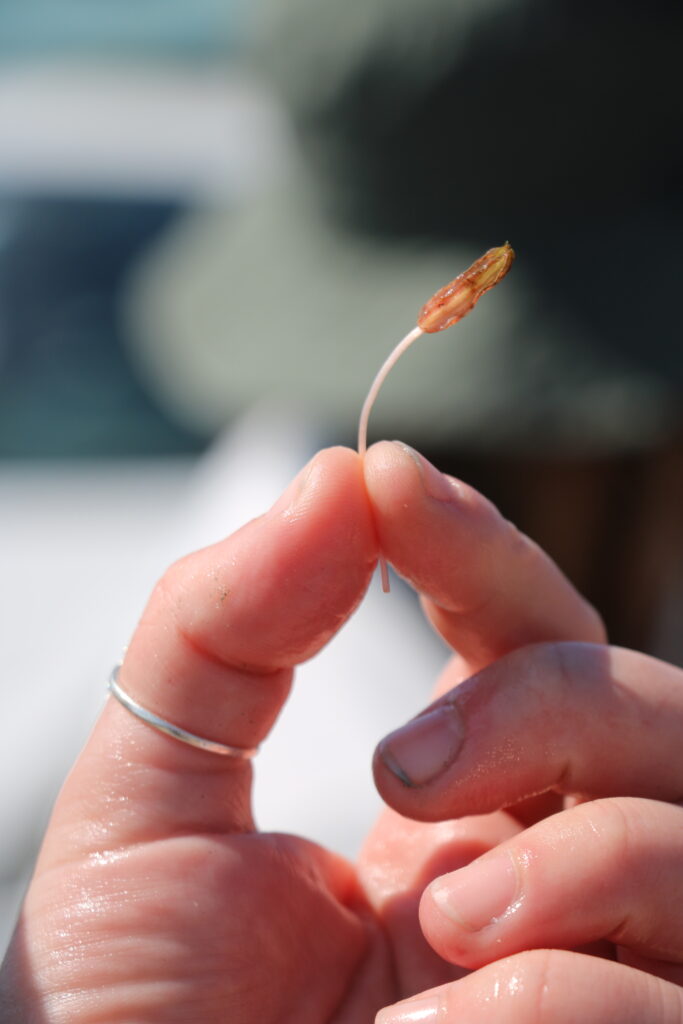
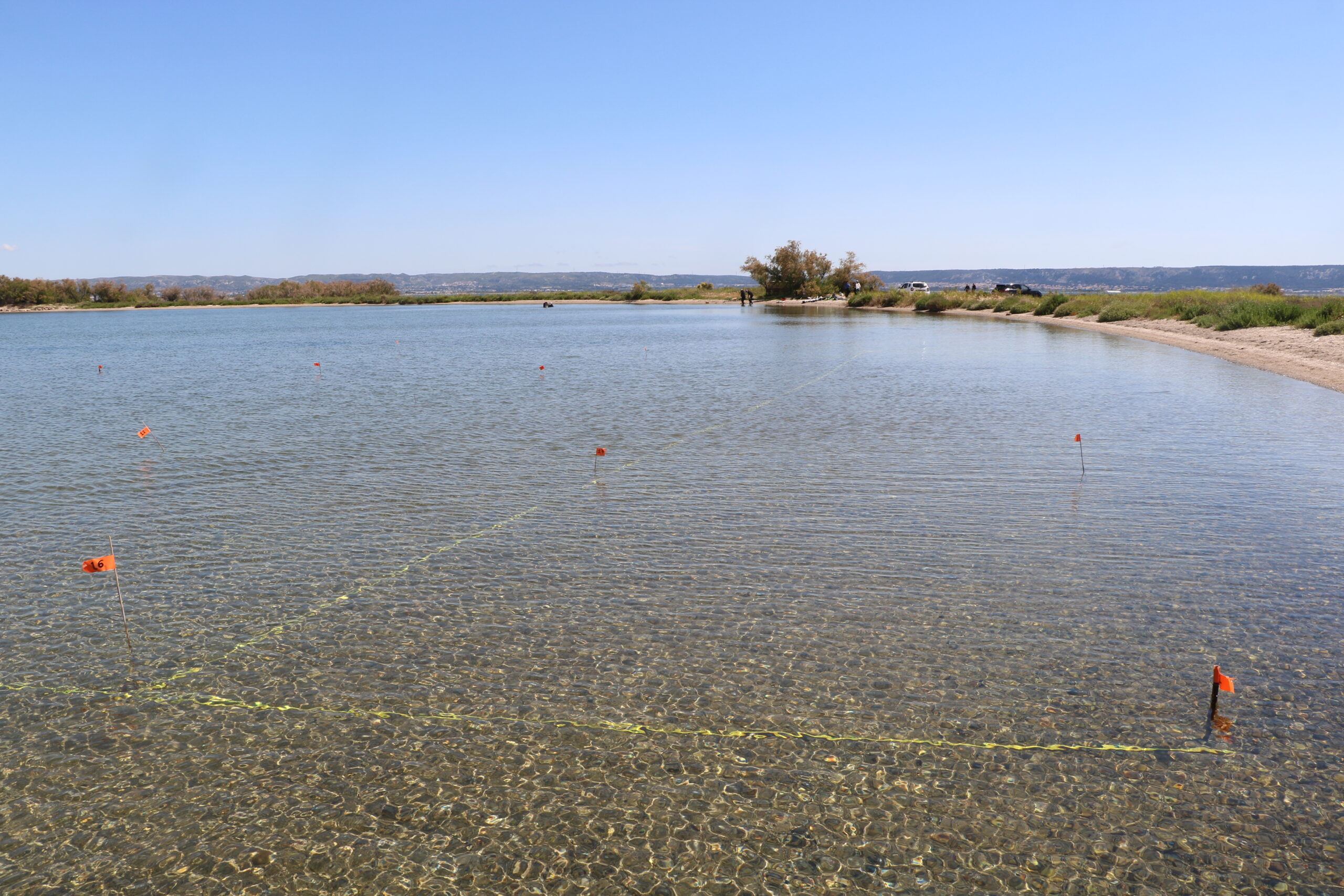
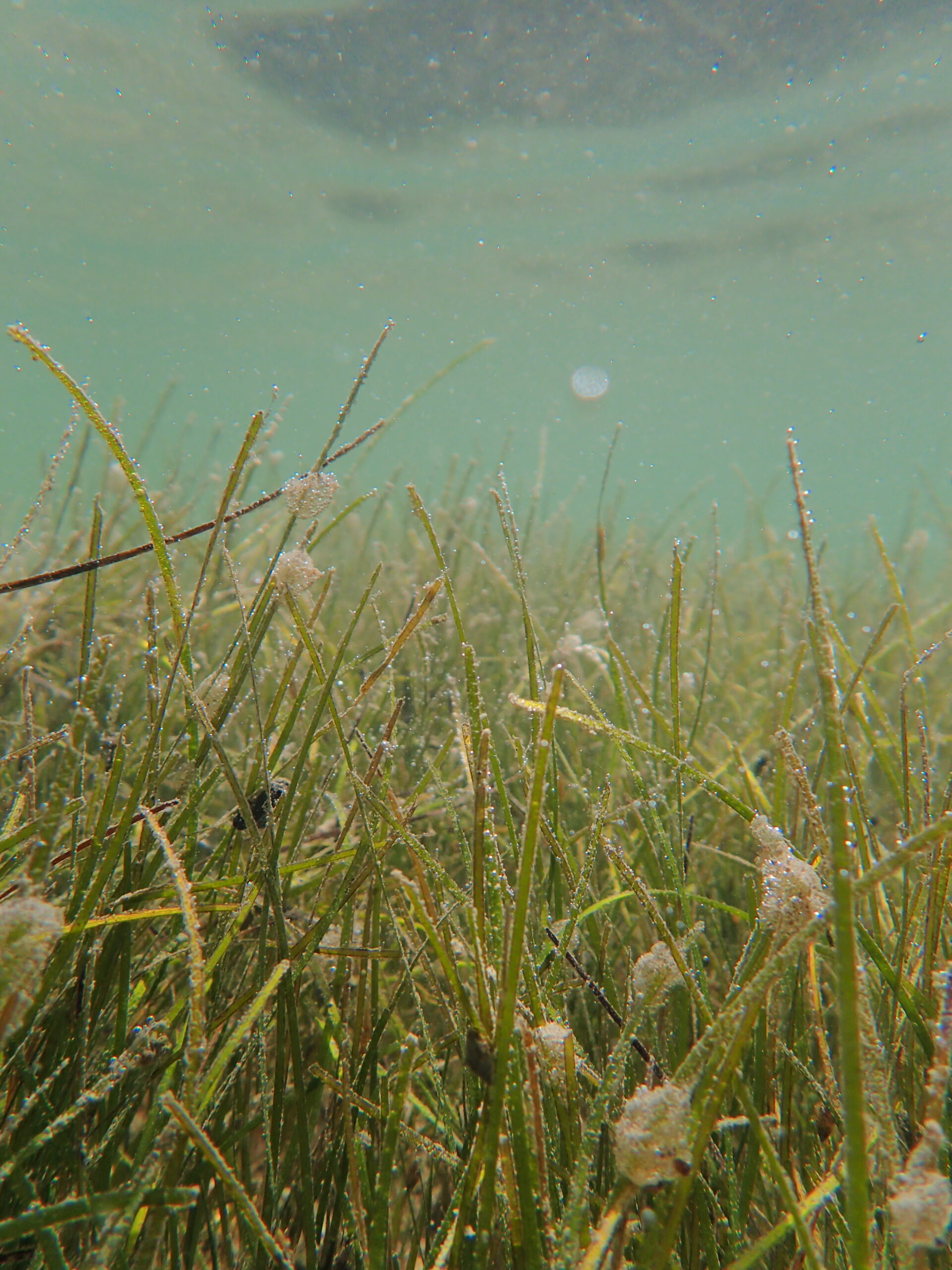
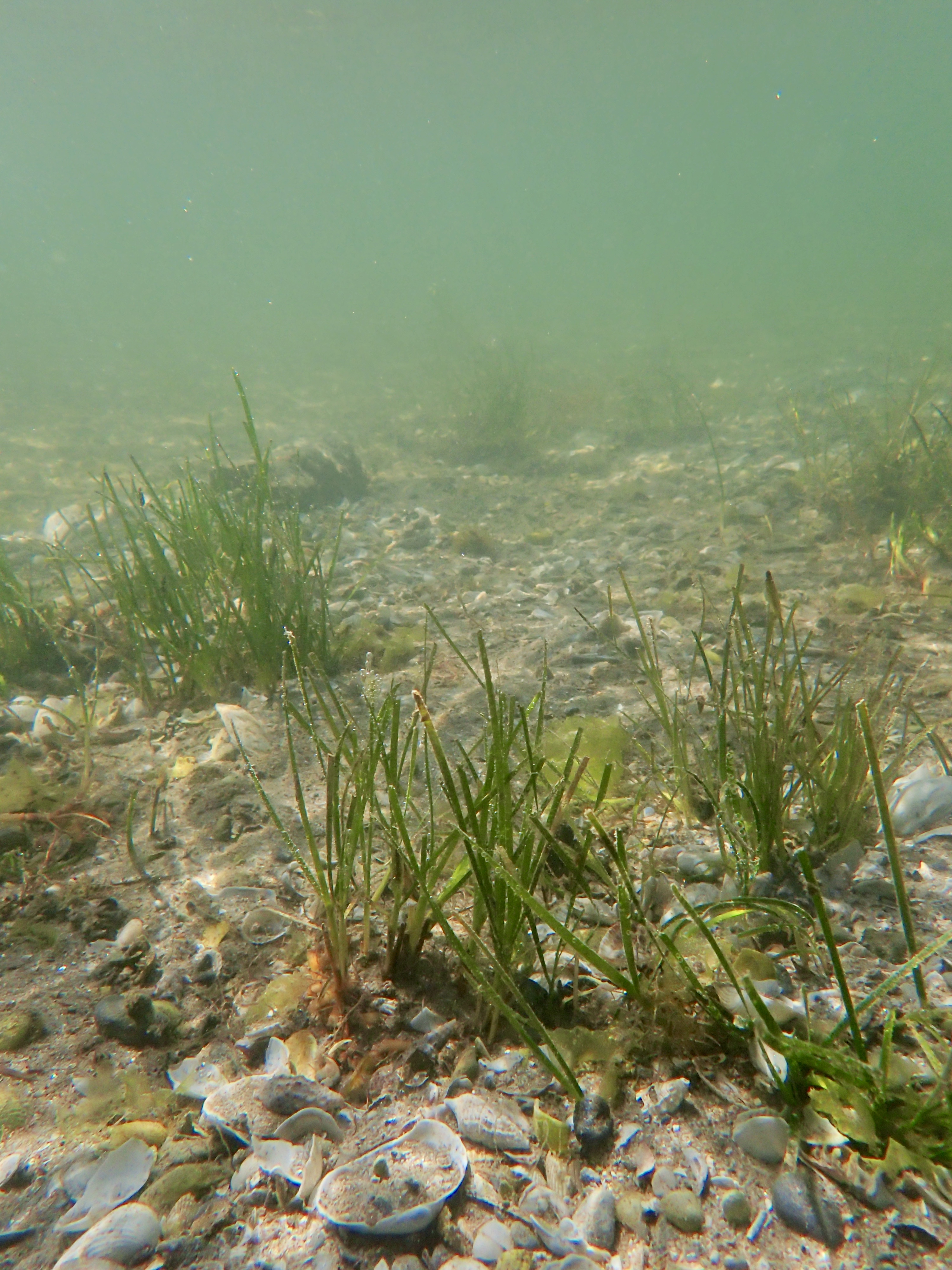
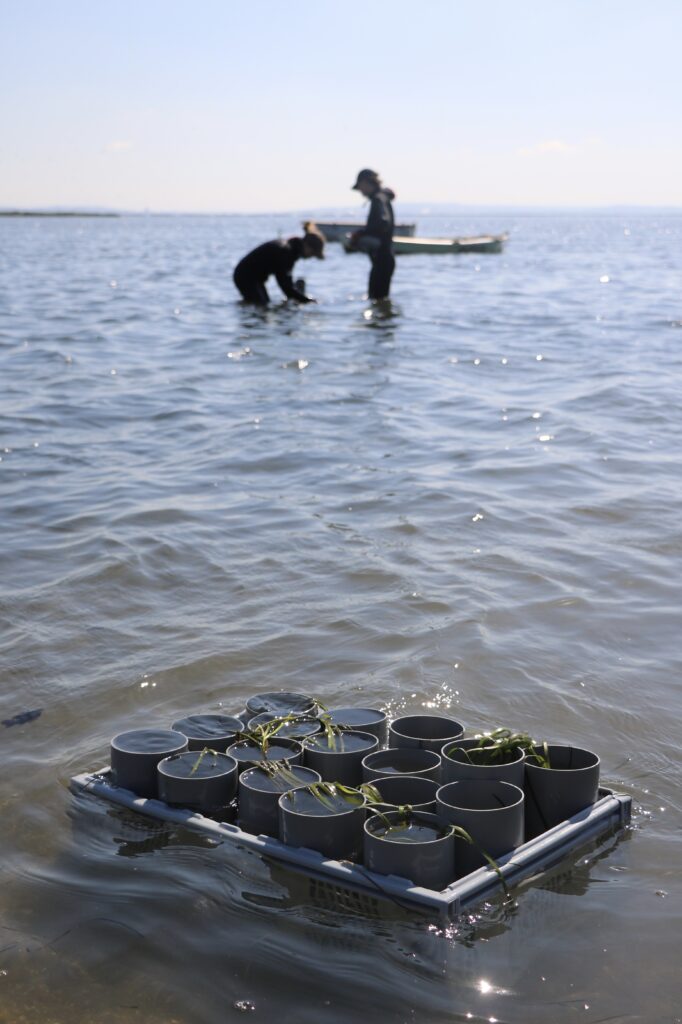








Local Partners and Initiatives
The seagrass restoration in l’Étang de Berre relies on a close collaboration with, and the expertise of, a number of local partners and initiatives.
GIS Posidonie
Since the 1990s, the macrophyte communities of the Étang de Berre has been the focus of annual monitoring by the GIS Posidonie and the GIPREB.
This annual monitoring of macrophytes covers the whole of the Étang de Berre with 31 study stations located around the perimeter of the lagoon.


Scientific collaborations
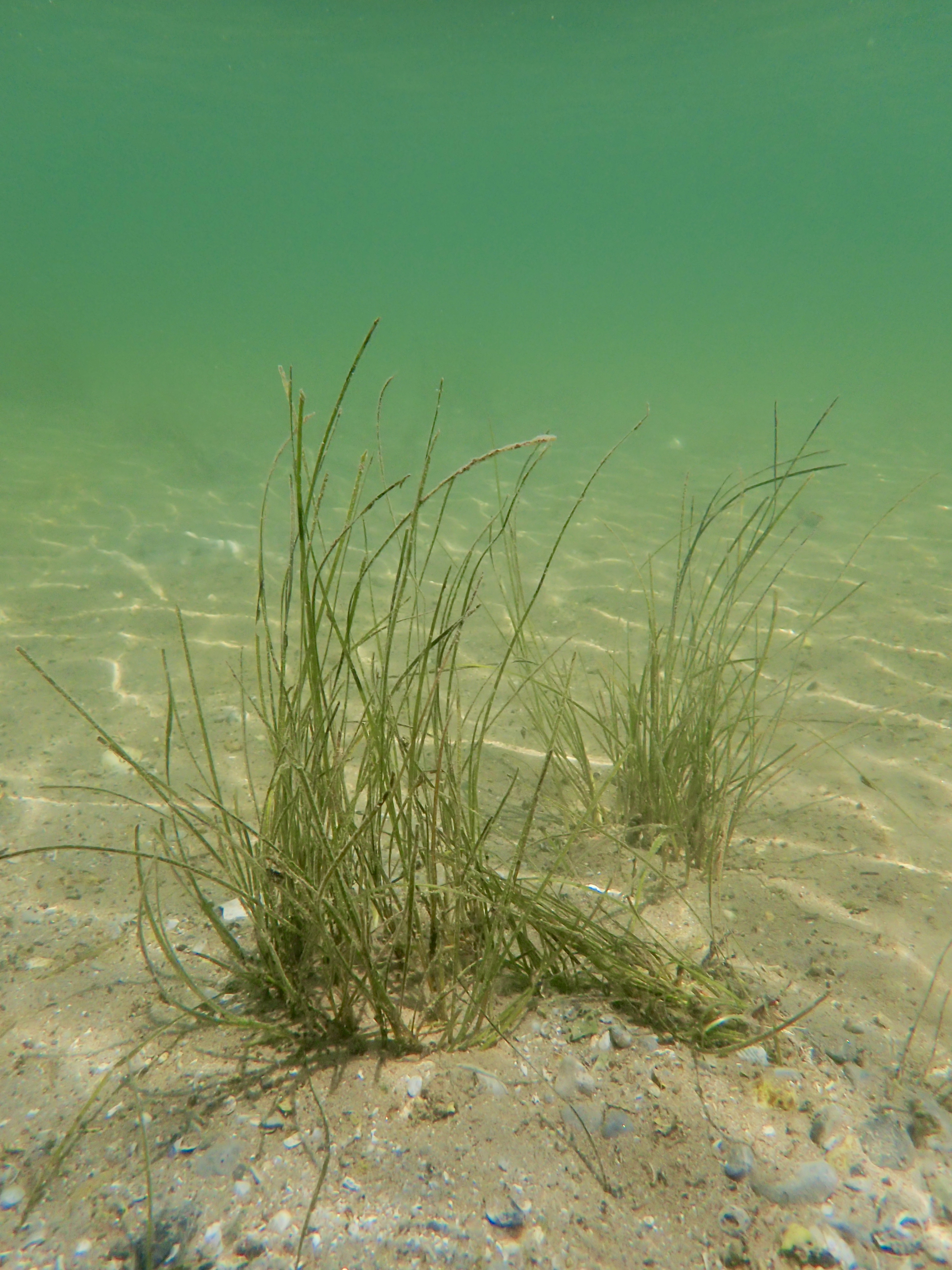
What if we could shield young seagrass plants germinating from seed by transplanting older plants around them? This European collaboration is testing whether an outer barrier (a U shaped ‘hug’) of seagrass helps seedlings of either the same or different species grow better inside.
Similar experiments are being replicated at several sites across Europe including in the Étang de Berre, Bay of Santander, in Mallorca and in the UK.
Science, collaboration, and restoration, all wrapped into one hug.
8 Vies pour la planète
8 Vies pour la planète is a non-profit organization (Association 1901) based in Saint-Chamas, that promotes environmental innovations and sustainable development.
Since 2018, 8 Vies have been developing technical, artistic, recreational, and participatory projects aimed at helping rebuild biodiversity, raise public awareness of environmental conservation issues, and promote more sustainable consumption patterns.
The association designs and leads numerous educational and fun environmental education workshops for a wide audience, particularly young people.


The Ocean Gardeners
The Ocean Gardeners is a programme of the European Seagrass Restoration Alliance (ESRA).
Through this programme ESRA are working to develop a more inclusive and diverse environmental movement by building public involvement and civic engagement in seascape restoration programmes.
Restoration Overview
Discover the detailed restoration phases, providing insight into site-specific actions and progress monitoring led by the Seagrass Consortium.
Phase One: Site Assessment
Initial evaluation of site conditions and ecological factors critical for planning effective seagrass restoration efforts.
Phase Two: Restoration Implementation
Execution of restoration activities including planting, habitat enhancement, and continuous site management.
Phase Three: Monitoring & Reporting
Ongoing monitoring to assess seagrass recovery, ensuring the restoration goals are met and informing future improvements.


